Abstract
Introduction.NPM1mut MRD assessment has been established as an independent prognostic marker in AML. The magnitude of NPM1mut MRD reduction post chemotherapy is associated with clinical outcome. At the Alfred and Austin Hospitals (Melbourne, Australia), high-dose cytarabine (HiDAC)-based induction was employed in favor of standard-dose cytarabine (SDAC) "7+3" induction until 2017. We hypothesized that HiDAC-based AML induction would result in greater reduction in NPM1mut MRD compared to SDAC-based induction and be associated with improved clinical outcome.
Methods. Consecutive patients (pts) with newly diagnosed NPM1 mutated AML were retrospectively identified from 2 institutions if NPM1mut MRD results were available after achieving morphologic remission. This study was approved by the Alfred HREC (460/17). The HiDAC cohort received either high (HDAC+3, 3 g/m2 BD d1,3,5,7, from 2012 to 2014) or intermediate dose cytarabine (IDAC+3, 1.5 g/m2 BD d1,3,5,7, from 2014 to 2017), in combination with idarubicin (12 mg/m2 d1-3). The SDAC cohort received 7+3 (from 2017 to March 2020). Planned consolidation chemotherapy for the HiDAC cohort consisted of 2 cycles of IcE (idarubicin 9 mg/m2 d1-2, cytarabine 100 mg/m2 d1-5, and etoposide 75 mg/m2 d1-5), whereas in the SDAC induction cohort, either 2 cycles of IDAC+2 (cytarabine 1 g/m2 x6 doses and idarubicin 12 mg/m2 d1-2), or 4 cycles of HiDAC (cytarabine 1-3 g/m2 x6 doses) was administered. Midostaurin was available as standard of care since December 2018 in Australia. NPM1mut bone marrow copy numbers by RT-qPCR are expressed per 105ABL1 copies.
Results. A total of 66 pts with NPM1mut AML were included in this study and summarized in Table. Majority had intermediate risk (95%) or normal karyotype (82%) and 38% had FLT3-ITD. The HiDAC cohort (n=28) was younger than the SDAC cohort (n=38) (median 47 vs 62 years) and more commonly underwent allogeneic HSCT in first remission (29% vs 5%). Among the HiDAC cohort, 54% completed the planned 2 cycles of consolidation chemotherapy, whereas 74% in the SDAC cohort completed at least 2 cycles of consolidation. Midostaurin was received by 9 pts, all from the SDAC cohort (24%).
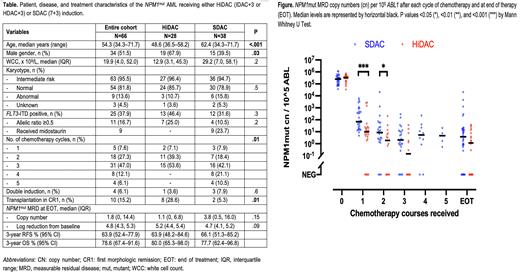
Baseline NPM1mut copy numbers were similar between both cohorts (Figure). Following course 1, the HiDAC cohort achieved a lower NPM1mut MRD level than the SDAC cohort: median 10 vs 82 copy numbers (p<0.001), 4.5 vs 3.4-log10 reduction (p<0.001), and 20% vs 0% with negative MRD (p=0.01). These differences narrowed after course 2: 1.9 vs 7.9 copies (p=0.05), 5.2 vs 4.4-log10 reduction (p=0.01), and 33% vs 10% with negative MRD (p=0.1). Similar findings were observed after course 3. The MRD levels at end of therapy (EOT) were similar between HiDAC and SDAC cohorts: 1.1 vs 3.8 copies (p=0.15), 5.2 vs 4.7-log10 reduction (p=0.09), and 41% (9/22) vs 22% (8/36) with negative MRD (p=0.15) (Figure).
Survivors were followed up for a median of 30 months: 18 pts had relapsed AML, 12 died, and median RFS and OS were both not reached. Early death (<60 days) was observed in only 1 pt (SDAC cohort). Estimated 3-year RFS and OS were 64% and 79%, respectively, without significant differences between the HiDAC vs SDAC induction cohorts: 3-year RFS 64% vs 66% and OS 80% vs 78%. Significant prognostic factors from univariate analyses were age (for RFS only), FLT3-ITD and MRD levels. Sensitivity analysis excluding the 9 pts who received midostaurin did not affect the results.
Next, we analyzed the prognostic significance of NPM1mut MRD response within each cohort of induction chemotherapy intensity. In the HiDAC cohort, NPM1mut MRD levels post course 1 (and 2), but not at EOT, were significantly associated with both risks of relapse (HR 0.31, 95% CI 0.15-0.67) and death (HR 0.31, 95% CI 0.14-0.70). Among the SDAC cohort, the log reduction at EOT, but not post course 1 and 2, was significantly associated with relapse (HR 0.47, 95% CI 0.26-0.84) and death (HR 0.45, 95% CI 0.22-0.89). Peripheral blood NPM1mut MRD levels were not available for comparison.
Conclusions. Intensified induction chemotherapy resulted in more rapid early NPM1mut MRD reduction but did not have significant impact on EOT MRD levels or survival outcomes. The clinical significance of MRD reduction at various time points should be interpreted in the context of selected therapeutic regimens. Moreover, MRD thresholds should be re-validated in the context of regimens incorporating novel targeted therapies.
Disclosures
Tiong:Servier: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau. Fielding:World Health Organization: Consultancy; Haematology Society of Australia and New Zealand: Research Funding. Fong:Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Otsuka: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Wei:Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene-BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties: Employee of the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and is eligible for a fraction of the royalty stream related to Venetoclax, Research Funding; Jazz: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal